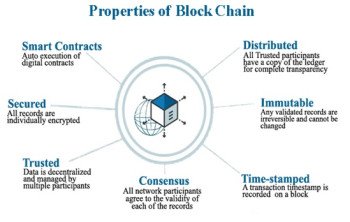
Artificial Intelligence (AI) can
significantly enhance Customer Relationship Management (CRM) software by
automating tasks, providing predictive insights, and improving customer
interactions. Here are some ways AI can improve CRM, along with new AI-driven
features that could be added to improve CRM software:
1.
AI-Powered Lead Scoring and Prediction
- Current Improvement:
AI can analyze historical customer data to rank leads based on their
likelihood to convert, making sales teams more efficient.
- New Feature:
Implement dynamic lead scoring models that continuously evolve
based on real-time customer behavior (e.g., website activity, emails
opened). This feature could also suggest the best next actions for the
sales team, improving the chances of conversion.
2.
Customer Sentiment Analysis
- Current Improvement:
AI can analyze communication (emails, social media, chat) to assess
customer sentiment and help teams better manage their responses.
- New Feature:
Add emotional AI that not only tracks sentiment in text-based
communication but also analyzes customer voice calls or video interactions
to detect frustration, enthusiasm, or confusion, enabling proactive
customer support.
3.
Personalized Customer Experience
- Current Improvement:
AI can deliver personalized content recommendations based on customer
behavior and preferences.
- New Feature:
Incorporate a hyper-personalization engine that integrates
behavioral, transactional, and demographic data to provide deeply
personalized suggestions for products, services, or content at the exact
right moment during customer interactions.
4.
Predictive Analytics for Sales Forecasting
- Current Improvement:
AI can forecast sales based on historical data, seasonality, and market
trends.
- New Feature:
Introduce real-time predictive analytics that adapt to current
market conditions, emerging competitors, or economic shifts, providing
sales teams with updated, reliable forecasts.
5.
AI-Driven Customer Support
- Current Improvement:
Chatbots and virtual assistants can handle basic customer queries 24/7,
reducing the workload on human agents.
- New Feature:
Develop context-aware AI agents that understand the entire customer
journey, can seamlessly switch between channels (email, chat, voice), and
escalate issues to humans with detailed context, ensuring a smooth and
efficient resolution process.
6.
Automated Workflow Optimization
- Current Improvement:
AI can help automate routine tasks like data entry and updating customer
records.
- New Feature:
Add an AI task manager that can intelligently prioritize tasks for
sales or support teams based on urgency, importance, and customer value,
ensuring that high-value customers receive timely attention.
7.
Next-Best-Action Recommendations
- Current Improvement:
AI can recommend product offerings based on customer past behavior.
- New Feature:
Develop a next-best-action recommender that goes beyond product
suggestions by suggesting relevant conversation topics, potential
discounts, or outreach methods, based on a combination of customer
interaction data and market trends.
8.
Automated Customer Segmentation
- Current Improvement:
AI can categorize customers based on demographics and purchasing patterns.
- New Feature:
Implement dynamic segmentation, where AI continuously updates and
redefines customer segments based on real-time behavior, allowing for more
accurate targeting in marketing campaigns.
9.
Natural Language Processing (NLP) for Data Entry
- Current Improvement:
AI-powered speech-to-text helps reduce manual data entry.
- New Feature:
Build AI assistants capable of summarizing phone calls, emails, or
meetings directly into CRM records, extracting key points, and suggesting
next steps, saving significant time for sales reps.
10.
AI-Enhanced Email Campaigns
- Current Improvement:
AI can optimize email campaigns by predicting the best time to send
messages.
- New Feature:
Introduce AI-driven A/B testing where the system autonomously tests
different email formats, subject lines, and call-to-action buttons and
learns over time which strategies work best for different customer
segments.
11.
Advanced Fraud Detection
- Current Improvement:
AI can detect fraudulent transactions or suspicious behavior patterns.
- New Feature:
Incorporate real-time fraud detection and risk analysis that adapts
as new behaviors and patterns emerge, reducing false positives and
enabling better protection for sensitive customer data.
12.
AI-Driven Voice Assistants for Sales Teams
- Current Improvement:
AI can assist in meeting preparation by surfacing relevant information
from the CRM.
- New Feature:
Develop intelligent voice assistants that can join meetings or
calls, take notes, suggest responses based on customer questions, and
update the CRM with follow-up tasks automatically.
13.
Churn Prediction and Prevention
- Current Improvement:
AI can predict customer churn based on past behavior.
- New Feature:
Combine churn prediction with proactive engagement, where AI not
only identifies potential churners but also triggers personalized
retention campaigns (emails, offers, check-ins) to re-engage customers at
risk.
14.
Augmented Sales Coaching
- Current Improvement:
AI can analyze sales team performance and suggest improvements.
- New Feature:
Introduce real-time coaching assistants that provide feedback
during customer calls (e.g., speech pacing, recommended talking points) or
after meetings, offering suggestions on how to improve future
interactions.
15.
AI-Enhanced Data Privacy Compliance
- Current Improvement:
AI helps manage customer data in compliance with privacy regulations.
- New Feature:
Build intelligent privacy engines that automatically detect and
anonymize sensitive data, help manage consent forms, and ensure CRM data
complies with evolving global privacy laws (GDPR, CCPA).
By incorporating these advanced AI
features, CRM systems can provide deeper insights, boost team productivity, and
deliver more personalized customer experiences, giving companies a significant
competitive advantage.
Dynamic lead scoring using LLM (Large
Language Models) is an advanced AI approach that
leverages the power of language models like GPT (Generative Pre-trained
Transformers) to analyze and understand customer behavior, communication
patterns, and other unstructured data sources to score leads dynamically.
Here's a detailed look at how
dynamic lead scoring using LLM models can enhance CRM systems:
1.
Analyzing Unstructured Data
- Challenge:
Traditional lead scoring often relies on structured data such as
demographic information, past purchase history, or interaction frequency.
- LLM Solution:
LLMs can process unstructured data such as emails, social media posts,
customer inquiries, and sales calls. This allows the model to assess a
customer’s intent, sentiment, and engagement level based on natural
language input, providing deeper insights than structured data alone.
Example: Analyzing emails or social media posts, the LLM could
detect positive or negative sentiment, urgency, and intent to buy, adjusting
the lead score in real-time.
2.
Context-Aware Lead Scoring
- Challenge:
Static lead scoring models don't account for evolving contexts, such as
market conditions or recent interactions.
- LLM Solution:
By constantly analyzing interactions across multiple channels (email,
social media, website, calls), LLMs can provide a context-aware lead
score that adapts based on the latest interactions. For example, if a
lead shows renewed interest after months of inactivity (e.g., opening
emails or revisiting the website), the LLM model can adjust their score
accordingly.
Example: A potential customer who asked several detailed product
questions on a call and later followed up with a long email could see their
lead score increase dynamically due to the LLM interpreting these actions as
high interest.
3.
Sentiment and Intent Detection
- Challenge:
Traditional lead scoring models don’t capture nuanced language signals
such as a customer’s excitement or frustration.
- LLM Solution:
LLMs, through natural language processing (NLP), can detect
sentiments like enthusiasm, urgency, or dissatisfaction, and update lead
scores accordingly. For example, if a lead expresses dissatisfaction with
a competitor, their score might rise because of the potential for a
switch.
Example: A customer saying "I'm really unhappy with my current
provider and looking for alternatives" can trigger an increase in their
lead score, signaling high potential for conversion.
4.
Real-Time Lead Score Updates
- Challenge:
Traditional lead scoring models update periodically and don't respond in real-time.
- LLM Solution:
LLM-based systems can analyze interactions in real-time (such as live
chat, customer inquiries, or social media posts) and adjust lead scores
instantly. This enables sales teams to respond to "hot leads"
immediately rather than waiting for batch score updates.
Example: If a lead engages in a live chat and expresses strong
interest, the LLM can instantly increase the lead score and notify the sales
team to act quickly.
5.
Incorporating Behavioral Signals
- Challenge:
Traditional models often rely heavily on demographic data, overlooking
behavioral signals like engagement with content.
- LLM Solution:
LLMs can evaluate engagement metrics by interpreting the tone and intent
behind a lead’s communications (e.g., how they interact with marketing
emails, web content, or sales outreach). This allows for more nuanced
scoring based on behavior.
Example: A lead that asks detailed, technical questions in an email
might be scored higher than one who only skims marketing materials, even if
both leads initially had similar static scores.
6.
Multi-Channel Data Fusion
- Challenge:
Most traditional models struggle to integrate data from diverse channels
(email, chat, social media).
- LLM Solution:
LLMs can be trained on datasets spanning multiple channels to extract
insights from conversational data, website logs, CRM records, and
even competitor mentions. This holistic view can be leveraged for more
accurate lead scoring.
Example: The LLM could score a lead based on their LinkedIn
activity (engagement with company posts), social mentions, as well as direct
interactions like emails or live chats, providing a more complete view of the
lead’s interest and engagement level.
7.
Identifying Hidden Opportunities
- Challenge:
Traditional models may miss subtle signals that indicate a lead's interest
or purchasing intent.
- LLM Solution:
LLMs can identify hidden opportunities by uncovering patterns or intent
that would go unnoticed in traditional models. For instance, subtle
phrases or recurring questions that hint at growing interest in a product
can be flagged, leading to a dynamic increase in the lead score.
Example: A lead repeatedly asking questions about pricing,
competitors, or implementation challenges might not see a significant score
increase in a traditional model, but an LLM could interpret this as a buying
signal and dynamically adjust the score.
8.
Automated Content Personalization
- Challenge:
Traditional lead scoring systems rarely influence content personalization
for sales outreach.
- LLM Solution:
In addition to scoring leads, LLMs can suggest personalized content based
on the lead’s interaction history, preferences, and behavior. For example,
if a lead frequently asks about certain features, the LLM could recommend
that the sales rep focus on those in their next outreach.
Example: A lead who consistently asks about product integration in
emails or chats would trigger the LLM to suggest sending case studies focused
on integration capabilities, along with a personalized sales pitch.
9.
Lead Conversion Probability Modeling
- Challenge:
Standard models calculate lead scores but often lack a robust mechanism to
model conversion probability.
- LLM Solution:
LLMs can build on dynamic lead scoring by analyzing historical
interactions and behaviors to predict the conversion likelihood of
a given lead. The model could assess the totality of interaction patterns
(e.g., frequency, engagement type, sentiment) and assign a probability
score for conversion.
Example: After interacting across multiple touchpoints (email,
website visits, social media), the LLM could predict that a lead has an 85%
likelihood to convert in the next 30 days, allowing the sales team to
prioritize them.
Key
Benefits of LLM-Based Dynamic Lead Scoring:
- Greater Accuracy:
With the ability to analyze unstructured and multi-channel data, LLMs
offer much more accurate and nuanced lead scores than traditional models.
- Real-Time Insights:
Sales teams can get lead score updates immediately, helping them
prioritize the most promising leads without delay.
- Deeper Understanding:
Sentiment and intent detection give a better sense of where the lead is in
their buying journey, providing more targeted and effective engagement
strategies.
- Automation and Personalization: LLMs can not only score leads dynamically but also recommend
personalized content or actions for sales teams to take, reducing the need
for manual input.
By integrating LLM-based dynamic
lead scoring into CRM systems, organizations can unlock the full potential of
AI to enhance lead management, increase conversion rates, and ultimately drive
more revenue.
Using Large Language Models
(LLMs) in CRM (Customer Relationship Management) software can dramatically
enhance how businesses manage customer interactions, streamline workflows, and
extract meaningful insights from vast amounts of unstructured data. Here’s how
LLM models can be effectively used in CRM systems:
1.
Automated Customer Support (Chatbots and Virtual Assistants)
- Function:
LLMs can power advanced customer support systems, providing conversational
AI that understands natural language, context, and customer intent.
- Benefit:
They offer instant, human-like responses to customer queries across
channels like chat, email, and voice, reducing the workload on human
agents.
- Example:
A customer asks about product compatibility, and the LLM understands the
context and provides a relevant, accurate answer while also suggesting
related products or services.
2.
Sentiment and Intent Analysis
- Function:
LLMs can analyze customer interactions (emails, chat logs, phone calls) to
detect sentiment (positive, neutral, or negative) and intent (inquiry,
complaint, interest).
- Benefit:
This helps CRM systems flag potential issues or high-interest leads,
allowing sales or support teams to prioritize responses and take proactive
actions.
- Example:
The system detects frustration in a customer email, escalating the case to
a senior support agent for faster resolution, or detects interest and
recommends timely follow-up by the sales team.
3.
Dynamic and Personalized Customer Engagement
- Function:
LLMs can personalize communication with customers by analyzing past
interactions, preferences, and purchasing behavior to recommend specific
content, products, or actions.
- Benefit:
Personalized outreach increases engagement and conversion rates. LLMs can
craft highly tailored emails, suggest the next best action, or recommend
products based on customer profiles.
- Example:
After analyzing a customer’s past purchases and browsing history, the LLM
drafts a personalized email offering a discount on a product the customer
is likely interested in.
4.
Advanced Lead Scoring and Qualification
- Function:
LLMs can dynamically score and qualify leads by analyzing a range of
inputs, including interactions, email communication, social media
activity, and sentiment analysis.
- Benefit:
This allows CRM systems to prioritize the most promising leads in
real-time based on more granular, nuanced data, helping sales teams focus
on high-potential customers.
- Example:
The system analyzes a lead’s engagement patterns (e.g., frequent email
interactions, positive sentiment) and assigns a higher lead score,
suggesting immediate follow-up by a sales rep.
5.
Intelligent Email and Communication Summarization
- Function:
LLMs can summarize lengthy emails, customer interactions, or meeting notes
into concise, actionable points.
- Benefit:
This reduces the cognitive load on CRM users by helping them quickly grasp
key details from customer communications and focus on next steps.
- Example:
A salesperson reviews a summary generated by an LLM for a long email
thread with a client, highlighting key discussion points and suggested
follow-ups, saving time while ensuring no important details are missed.
6.
Automated Data Entry and Enrichment
- Function:
LLMs can automate the extraction of relevant information from customer
emails, chats, and other interactions, then populate CRM fields with key
data points such as contact details, preferences, and issues.
- Benefit:
This reduces manual data entry errors and saves time for users, allowing
them to focus on higher-value tasks.
- Example:
After a customer inquiry email, the LLM extracts the customer’s name,
issue type, and contact information, then automatically updates the CRM
record without human intervention.
7.
Customer Journey Mapping and Prediction
- Function:
LLMs can analyze all touchpoints in a customer’s journey (emails, calls,
social media interactions, website visits) to predict the next stages of
the journey and recommend actions to move customers closer to purchase or
resolution.
- Benefit:
This provides businesses with foresight on customer needs and behaviors,
allowing them to optimize marketing, sales, and support efforts at the
right time.
- Example:
The LLM predicts that a lead will likely convert within the next two weeks
based on engagement patterns and recommends sending a special offer or
discount to accelerate the process.
8.
Multi-Channel Interaction Analysis
- Function:
LLMs can unify and analyze customer interactions across multiple
channels—email, social media, phone calls, website interactions—providing
a complete, real-time view of customer behavior and intent.
- Benefit:
This allows sales and support teams to better understand customers’ needs
and respond more effectively by having a complete context for each
interaction.
- Example:
A customer tweets a complaint about a product, and the LLM connects this
with recent email support requests, identifying a potential retention
issue and alerting the customer success team.
9.
Churn Prediction and Retention Strategies
- Function:
LLMs can predict the likelihood of customer churn based on historical
interaction data, sentiment analysis, and engagement frequency.
- Benefit:
By identifying at-risk customers early, businesses can take proactive
retention actions such as personalized outreach or offering incentives to
prevent churn.
- Example:
The LLM analyzes declining engagement from a key account and predicts a
high risk of churn, prompting the sales team to offer a loyalty discount
or a personal call to re-engage the customer.
10.
Document and Knowledge Management
- Function:
LLMs can assist with document retrieval and summarization within CRM
systems, quickly finding relevant information from knowledge bases,
support documents, or past customer interactions.
- Benefit:
This helps support and sales teams access relevant information faster,
improving response times and service quality.
- Example:
A support agent asks the system for documentation on a specific technical
issue, and the LLM retrieves the most relevant knowledge base articles or
past resolutions from similar cases.
11.
Voice and Conversation Analysis
- Function:
LLMs can transcribe, analyze, and summarize voice conversations from sales
or support calls, extracting key details such as customer sentiment,
issues raised, and next steps.
- Benefit:
Voice interaction analysis helps CRM systems capture critical insights
from phone calls, which are often lost in traditional systems.
- Example:
After a sales call, the LLM transcribes the conversation, detects key
action items, and updates the CRM with the call summary and recommended
follow-up tasks.
12.
Automated Follow-Up Recommendations
- Function:
LLMs can analyze customer interaction history and recommend personalized
follow-up actions, including when to reach out and what message to send.
- Benefit:
This ensures that leads and customers receive timely and relevant
communication, improving engagement and conversion rates.
- Example:
After a lead interacts with a marketing campaign, the LLM suggests sending
a follow-up email with additional product details and a demo offer, based
on the lead’s engagement history.
Benefits
of Using LLMs in CRM Software:
- Enhanced Productivity:
Automating routine tasks like data entry, email generation, and
summarization saves time and reduces human error.
- Better Decision-Making: LLM-driven insights from customer interactions (e.g.,
sentiment analysis, behavior tracking) enable sales and support teams to
make data-driven decisions.
- Personalization at Scale: LLMs enable highly personalized customer experiences,
tailoring recommendations, emails, and offers to individual customer
preferences and behaviors.
- Improved Customer Retention: By identifying at-risk customers through churn
prediction and sentiment analysis, LLMs help businesses proactively
address issues and improve retention.
- Cost Savings:
Automating manual processes, reducing the need for manual data entry, and
providing intelligent suggestions can reduce operational costs and improve
efficiency.
By integrating LLMs into CRM
systems, businesses can provide more personalized customer interactions,
improve lead management, automate time-consuming tasks, and leverage powerful
insights from both structured and unstructured data.